In today’s tech-driven world, the terms Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are often used interchangeably—but they are not the same. Each represents a different level of advancement in the field of intelligent systems. Understanding the distinctions between them is key to grasping how technology is evolving and how it can be applied across industries.
This article breaks down these concepts in a clear, beginner-friendly way and shows how they relate to one another.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broadest concept. It refers to the ability of a machine or software to mimic human cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Key Characteristics of AI:
- Simulates human thinking
- Performs tasks autonomously
- Can be rule-based or data-driven
- Can include perception, motion, and reasoning
Common AI Examples:
- Voice assistants like Siri or Alexa
- Autonomous vehicles
- Smart home devices
- Fraud detection systems
AI is the umbrella under which Machine Learning and Deep Learning fall.
What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that enables machines to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed for every task.
How It Works:
ML algorithms use statistical techniques to identify patterns in data and make predictions or decisions based on that data.
Types of Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning: Trained on labeled data (e.g., spam vs. not spam)
- Unsupervised Learning: Finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data (e.g., customer segmentation)
- Reinforcement Learning: Learns through trial and error (e.g., game AI, robotic control)
Machine Learning in Action:
- Netflix recommending movies
- Email filters detecting spam
- Predictive maintenance in manufacturing
- Customer churn prediction
ML is powerful because it allows systems to adapt and improve as they are exposed to more data.
What Is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of Machine Learning that uses neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to model complex patterns in large volumes of data.
What Sets Deep Learning Apart:
- Mimics the structure of the human brain with artificial neural networks
- Requires large amounts of data and computing power
- Can process unstructured data like images, audio, and text
Deep Learning Applications:
- Facial recognition
- Speech-to-text systems
- Natural language processing (e.g., ChatGPT)
- Medical imaging diagnostics
- Self-driving cars
Deep Learning is the most advanced and data-intensive form of AI currently in mainstream use.
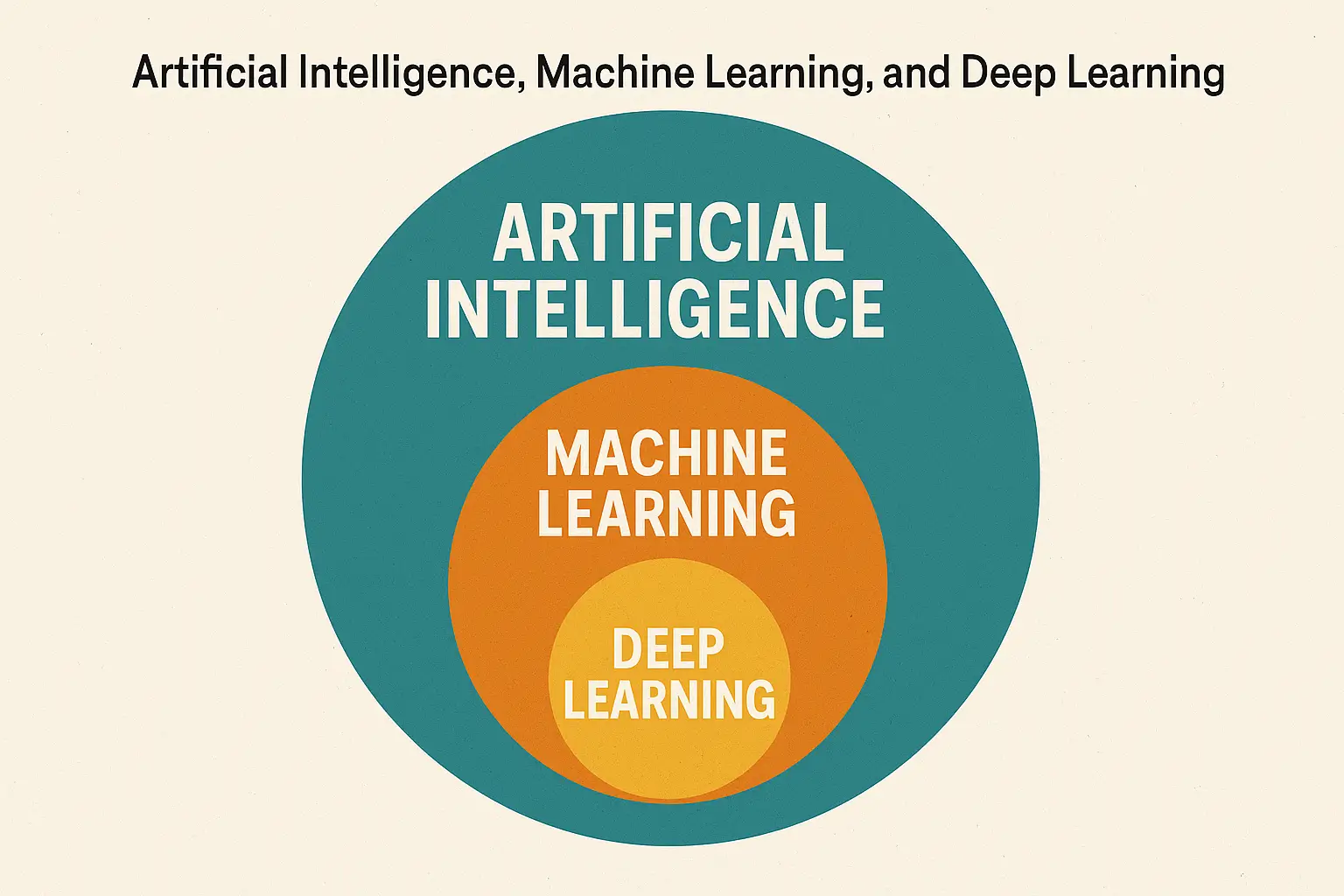
Visualizing the Hierarchy
Think of AI, ML, and DL like concentric circles:
- The largest circle is AI, the overall field.
- Inside it sits ML, a more specific area focused on data-driven learning.
- At the core is DL, the cutting-edge frontier using neural networks.
This structure shows how the technologies are nested and progressively more specialized.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad | Narrower | Most specific |
| Human Intervention | Can include manual rules | Learns from data | Learns from massive data sets |
| Data Requirements | Moderate | Moderate to high | Very high |
| Hardware Needs | Low to moderate | Moderate | High (often GPUs) |
| Examples | Chess-playing AI, Chatbots | Product recommendations, fraud detection | Voice assistants, facial recognition |
Which One Should You Learn?
If you’re exploring careers or skills in tech, your choice depends on your goals:
- For general business or tech roles: Start with AI basics and how it’s used in industries.
- For data analysis and predictions: Learn Machine Learning with Python, scikit-learn, or TensorFlow.
- For advanced AI systems: Dive into Deep Learning, using frameworks like PyTorch and working with large datasets.
Real-World Impact
Understanding these differences is not just academic—it’s practical. Companies use all three levels of AI to:
- Improve decision-making
- Automate customer service
- Predict trends and outcomes
- Enhance safety and personalization
By distinguishing between AI, ML, and DL, teams can apply the right technology for the right challenge.
Final Thoughts: Building a Foundation in AI
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning form a hierarchy of innovation. AI is the broad science of making machines smart. Machine Learning teaches machines how to learn. Deep Learning takes that learning to the next level by enabling machines to think in ways similar to humans.
Knowing the differences empowers you to navigate the tech world with confidence—whether you’re building a career, launching a product, or just staying informed.